什么是BlockingDeque?
BlockingDeque是继承BlockingDeque的接口,是一个基于链表的双端阻塞队列。
BlockingDeque主要方法行为

像BlockingQueue一样,BlockingDeque是线程安全的, 也不接受null元素,BlockingDeque可以是限制容量的,如果不指定容量,则会指定Integer.MAX_VALUE为默认值。
BlockingDeque可以直接用于BlockQueue FIFO队列,下图指明了BlockingDeque与BlockQueue中等价的方法:
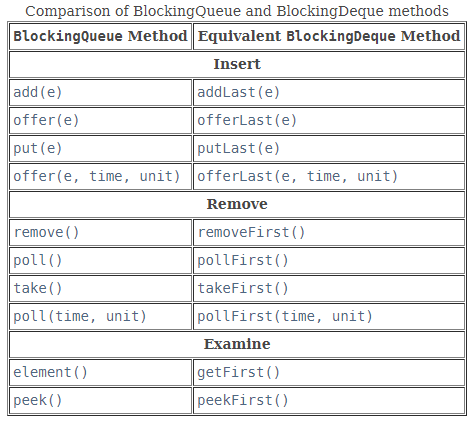
BlockingDeque主要实现类
- LinkedBlockingDeque
LinkedBlockingDeque是一个基于链表的双端阻塞队列。和LinkedBlockingQueue类似,区别在于该类在实现了BlockQueue的基础上,又实现了Deque接口。
LinkedBlockingDeque是一个可选容量的阻塞队列,如果没有设置容量,那么容量将是Integer.MAX_VALUE。
源码分析
重要字段
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
/** Number of items in the deque */
private transient int count;
/** Maximum number of items in the deque */
private final int capacity;
/** Main lock guarding all access */
final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Condition for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
/** Condition for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
从上面的字段,可以得到LinkedBlockingDeque内部只有一把锁以及该锁上关联的两个条件,所以可以推断同一时刻只有一个线程可以在队头或者队尾执行入队或出队操作。可以发现这点和LinkedBlockingQueue不同,LinkedBlockingQueue可以同时有两个线程在两端执行操作。
构造方法
public LinkedBlockingDeque() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public LinkedBlockingDeque(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public LinkedBlockingDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibility
try {
for (E e : c) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!linkLast(new Node<E>(e)))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
入队、出队方法
由于LinkedBlockingDeque是一个双端队列,所以就可以在队头执行入队和出队操作,也可以在队尾执行入队和出队操作,不过实现的方法基本类似,下面就以putFirst()为例,说明一下阻塞方法的执行过程:
public void putFirst(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
while (!linkFirst(node))
notFull.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
从上面的代码可以看到offerFirst()的流程:
- 不允许元素为null
- 首先获取锁,一旦获取到锁后,调用linkFirst()将节点插入在队头,最后释放锁。
linkFirst()的实现如下:
private boolean linkFirst(Node<E> node) {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
if (count >= capacity)
return false;
Node<E> f = first;
node.next = f;
first = node;
if (last == null)
last = node;
else
f.prev = node;
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
从上面可以看到,返回false只有在队列中元素满了的情况下;其他情况都会返回true,并且由于成功插入了一个节点,会调用notEmpty条件的signal()方法释放因队列中元素个数为0时的take线程。 关于一把锁,两个条件的实现方式和ArrayBlockingQueue的原理一样。
总结
LinkedBlockingDeque和LinkedBlockingQueue的相同点在于:
- 基于链表
- 容量可选,不设置的话,就是Int的最大值
和LinkedBlockingQueue的不同点在于:
- 双端链表和单链表
- 不存在哨兵节点
- 一把锁+两个条件
LinkedBlockingDeque和ArrayBlockingQueue的相同点在于:使用一把锁+两个条件维持队列的同步。
